CJ Biomaterials’ Amorphous Polyhydroxyalkanoate Gets Green Light from FDA for Food-Contact Applications
FDA listing clears the way for CJ Biomaterials’ aPHA to be used in the manufacture of food contact materials sold in the U.S.
Edited by Lilli Manolis Sherman

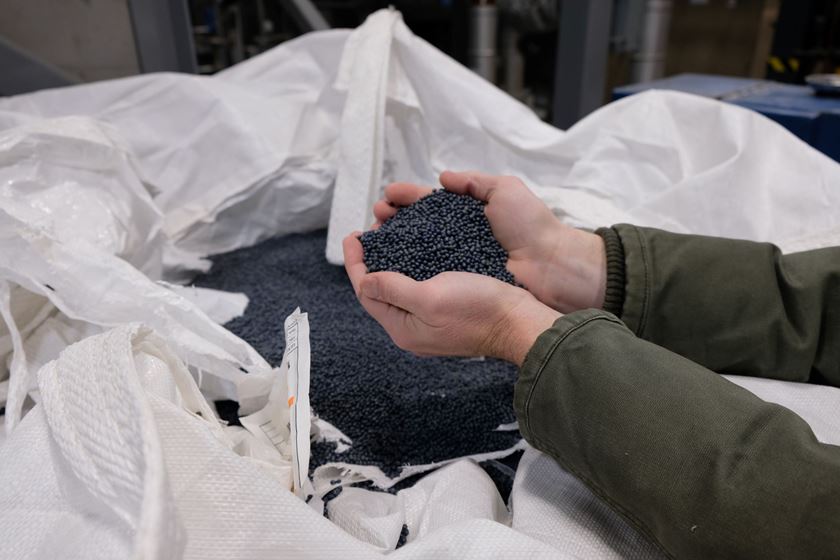
Amorphous polyhydroxyalkanoate (aPHA) produced by CJ Biomaterials, Inc., a division of South Korea-based CJ CheilJedang, is now included in FDA’s Inventory of Effective Food Contact Substances (FCS). Assigned Food Contact Notification (FCN) 2281, CJ Biomaterials’ aPHA, branded Phact A1000P, can now be used to make packaging materials sold in the U.S. that come into contact with food, including rigid and flexible packaging, serviceware and other products.
CJ Biomaterials was the world’s first company to produce amorphous PHA, which is a softer, more rubbery version of PHA that offers fundamentally different performance characteristics than crystalline or semi-crystalline forms of the biopolymer. It is a biobased material that is TUV OK certified for industrial and home compost, soil biodegradable and marine biodegradable. When combined with other biopolymers, such as PLA, it enhances the biodegradability and compostability of products, including food packaging materials.
CJ Biomaterials introduced its aPHA in early 2022, and the biopolymer is already being used to develop various end-use products, including cosmetic containers. The company has also partnered with various organizations to start developing other eco-friendly solutions using aPHA, including NatureWorks, Accor Hotels, and Yuhan-Kimberly, and plans to expand production capacity to meet expected demand for the material. Said CJ Biomaterials’ chief commercial officer Max Senechal, “Having Phact A1000P on the approved FCS inventory list means we can now expand the use of our amorphous PHA to a range of food contact materials in a key growth market, further advancing our goal to make a positive impact on the world."
RELATED CONTENT
-
Injection Molding Wood-Plastic Composites
Injection molders are just becoming acquainted with this new class of molding materials. It pays to learn some basic processing guidelines before jumping in.
-
Wood-Filled Plastics: They Need the Right Additives for Strength, Good Looks, and Long Life
Wood-plastic composites, or WPCs, are already a 1.3-billion-lb market and are growing at 20% annually.
-
Additive Manufacturing: Materials for ‘Real-World’ Parts
Developments in materials have helped pave the way for processors to make ‘real world’ parts from what is collectively known as 3D printing. Here’s a comprehensive review of the materials available.